AWS offers a comprehensive range of compute services from virtual machines to serverless functions. This guide covers EC2, Lambda, ECS, EKS, and Fargate with practical deployment examples using AWS CDK, CloudFormation, and Terraform.
This is Part 2 of a 6-part series covering AWS Cloud Platform for developers.
- Part 1: Fundamentals – Account Structure, IAM, Regions
- Part 2 (this article): Compute Services – EC2, Lambda, ECS, EKS
- Part 3: Storage & Databases – S3, RDS, DynamoDB
- Part 4: Networking – VPC, Route 53, CloudFront
- Part 5: Security & Compliance – KMS, WAF, Shield
- Part 6: DevOps & IaC – CDK, CloudFormation, Terraform
AWS Compute Services Overview
Choosing the right compute service depends on your workload characteristics, operational preferences, and cost optimization goals. AWS provides options ranging from full-control virtual machines to fully-managed serverless functions.
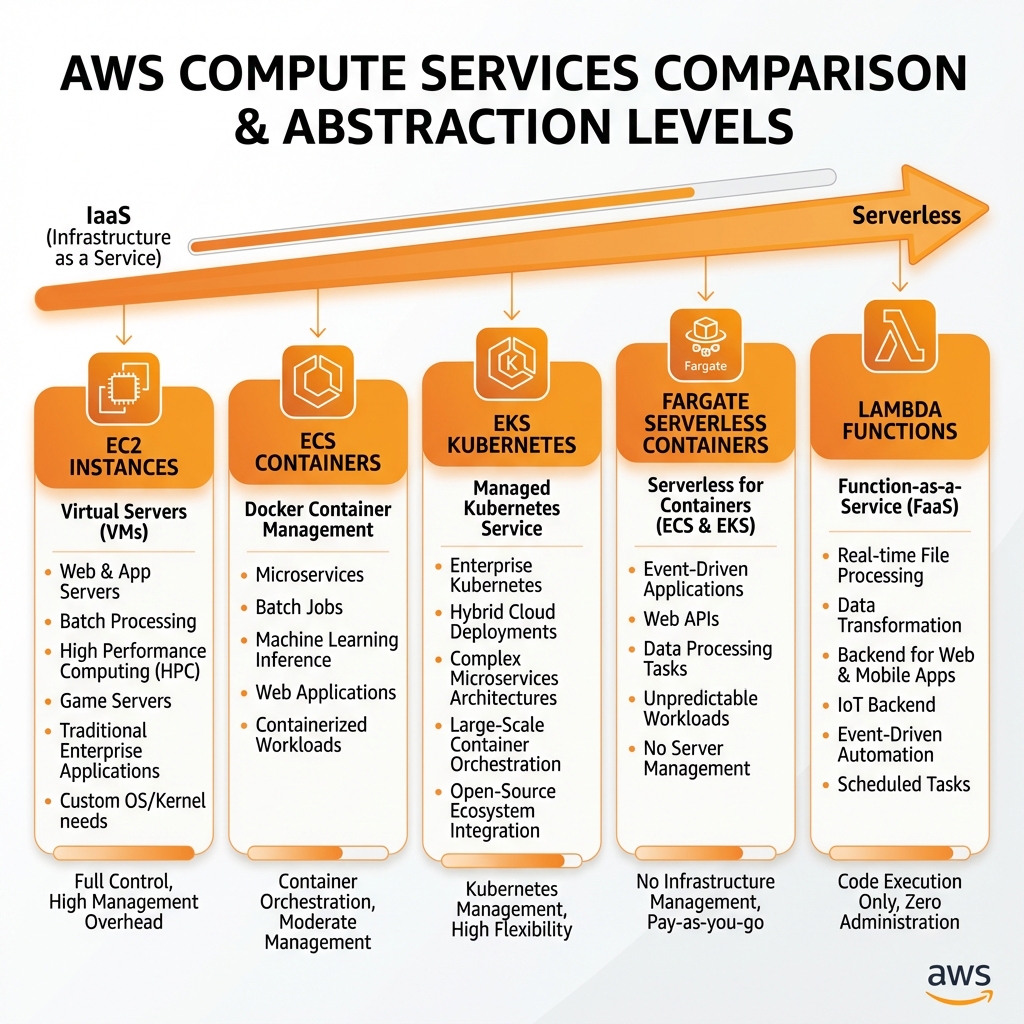
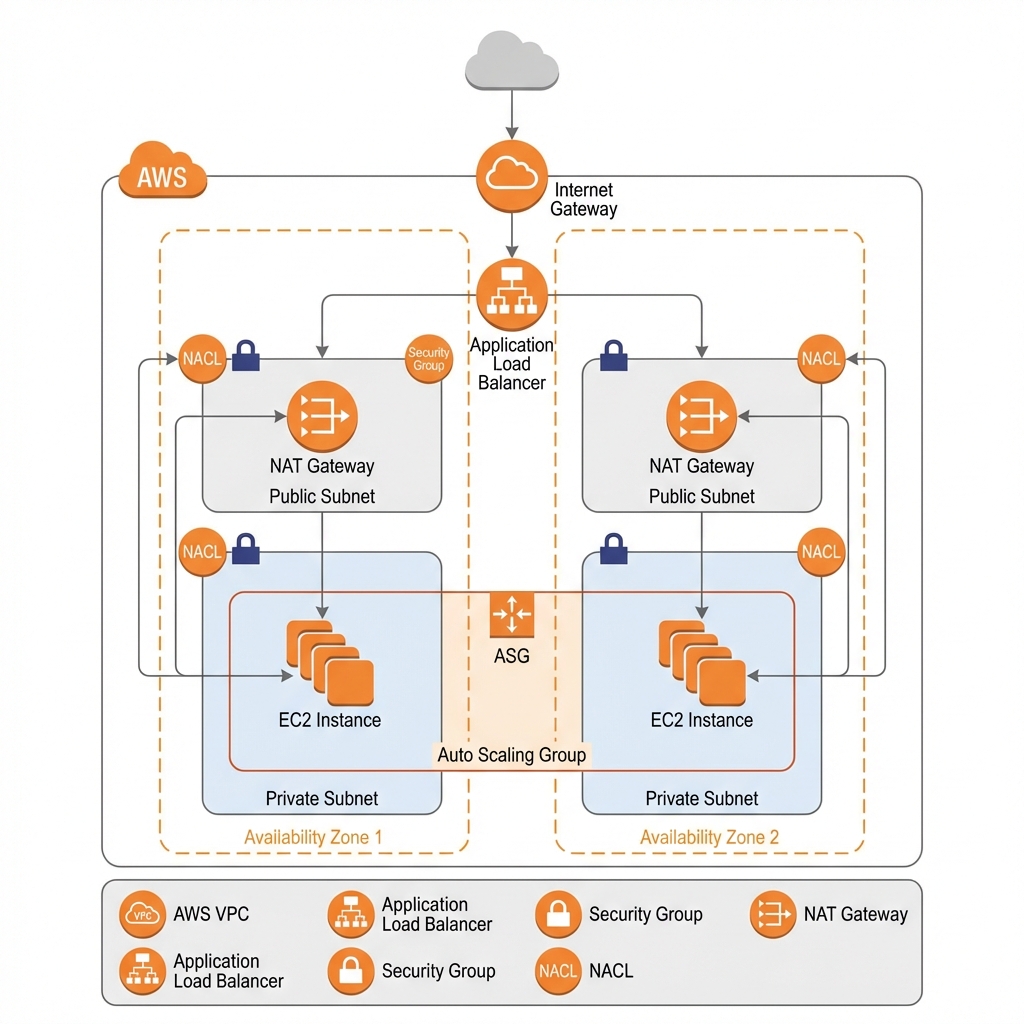
Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud)
EC2 provides resizable virtual servers (instances) in the cloud. You have complete control over the operating system, networking, and storage configuration.
Instance Types & Selection
| Family | Optimized For | Use Cases | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| M (General) | Balanced compute/memory | Web servers, app servers | m7i.large, m7g.xlarge |
| C (Compute) | High CPU performance | Batch processing, HPC | c7i.2xlarge, c7g.4xlarge |
| R (Memory) | High memory-to-CPU ratio | Databases, in-memory caching | r7i.4xlarge, r7g.8xlarge |
| P/G (GPU) | GPU acceleration | ML training, graphics | p5.48xlarge, g5.xlarge |
| T (Burstable) | Variable workloads | Dev/test, microservices | t3.micro, t4g.small |
EC2 with AWS CDK (TypeScript)
// AWS CDK: Production EC2 Auto Scaling Group
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import * as ec2 from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-ec2';
import * as autoscaling from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-autoscaling';
import * as elbv2 from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-elasticloadbalancingv2';
export class Ec2Stack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
// VPC with public and private subnets
const vpc = new ec2.Vpc(this, 'AppVpc', {
maxAzs: 3,
natGateways: 1,
subnetConfiguration: [
{ cidrMask: 24, name: 'Public', subnetType: ec2.SubnetType.PUBLIC },
{ cidrMask: 24, name: 'Private', subnetType: ec2.SubnetType.PRIVATE_WITH_EGRESS },
],
});
// Security group
const webSg = new ec2.SecurityGroup(this, 'WebSg', {
vpc,
description: 'Security group for web servers',
allowAllOutbound: true,
});
webSg.addIngressRule(ec2.Peer.anyIpv4(), ec2.Port.tcp(80), 'Allow HTTP');
// Launch template with user data
const userData = ec2.UserData.forLinux();
userData.addCommands(
'yum update -y',
'amazon-linux-extras install nginx1 -y',
'systemctl start nginx',
'systemctl enable nginx'
);
// Auto Scaling Group
const asg = new autoscaling.AutoScalingGroup(this, 'WebAsg', {
vpc,
instanceType: ec2.InstanceType.of(ec2.InstanceClass.T3, ec2.InstanceSize.MEDIUM),
machineImage: ec2.MachineImage.latestAmazonLinux2(),
minCapacity: 2,
maxCapacity: 10,
desiredCapacity: 2,
vpcSubnets: { subnetType: ec2.SubnetType.PRIVATE_WITH_EGRESS },
securityGroup: webSg,
userData,
healthCheck: autoscaling.HealthCheck.elb({ grace: cdk.Duration.minutes(5) }),
});
// CPU-based scaling
asg.scaleOnCpuUtilization('CpuScaling', {
targetUtilizationPercent: 70,
cooldown: cdk.Duration.minutes(5),
});
// Application Load Balancer
const alb = new elbv2.ApplicationLoadBalancer(this, 'WebAlb', {
vpc,
internetFacing: true,
});
const listener = alb.addListener('HttpListener', { port: 80 });
listener.addTargets('WebTargets', {
port: 80,
targets: [asg],
healthCheck: {
path: '/health',
interval: cdk.Duration.seconds(30),
healthyThresholdCount: 2,
unhealthyThresholdCount: 5,
},
});
new cdk.CfnOutput(this, 'AlbDns', { value: alb.loadBalancerDnsName });
}
}EC2 with Terraform
# Terraform: EC2 Auto Scaling with ALB
resource "aws_launch_template" "web" {
name_prefix = "web-"
image_id = data.aws_ami.amazon_linux_2.id
instance_type = "t3.medium"
network_interfaces {
associate_public_ip_address = false
security_groups = [aws_security_group.web.id]
}
user_data = base64encode(<<-EOF
#!/bin/bash
yum update -y
amazon-linux-extras install nginx1 -y
systemctl start nginx
systemctl enable nginx
EOF
)
iam_instance_profile {
name = aws_iam_instance_profile.web.name
}
monitoring {
enabled = true
}
tag_specifications {
resource_type = "instance"
tags = {
Name = "web-server"
Environment = var.environment
}
}
}
resource "aws_autoscaling_group" "web" {
name = "web-asg"
vpc_zone_identifier = aws_subnet.private[*].id
target_group_arns = [aws_lb_target_group.web.arn]
health_check_type = "ELB"
min_size = 2
max_size = 10
desired_capacity = 2
launch_template {
id = aws_launch_template.web.id
version = "$Latest"
}
instance_refresh {
strategy = "Rolling"
preferences {
min_healthy_percentage = 75
}
}
}
resource "aws_autoscaling_policy" "cpu" {
name = "cpu-scale"
autoscaling_group_name = aws_autoscaling_group.web.name
policy_type = "TargetTrackingScaling"
target_tracking_configuration {
predefined_metric_specification {
predefined_metric_type = "ASGAverageCPUUtilization"
}
target_value = 70.0
}
}- Default vCPU limit: 32 On-Demand per region (request increase)
- EBS volume limit: 5,000 per region
- Spot instances can be interrupted with 2-minute warning
- T3/T4g instances have CPU credits - monitor carefully
AWS Lambda (Serverless Functions)
Lambda runs code without provisioning servers. You're charged only for compute time consumed—there's no charge when your code isn't running.
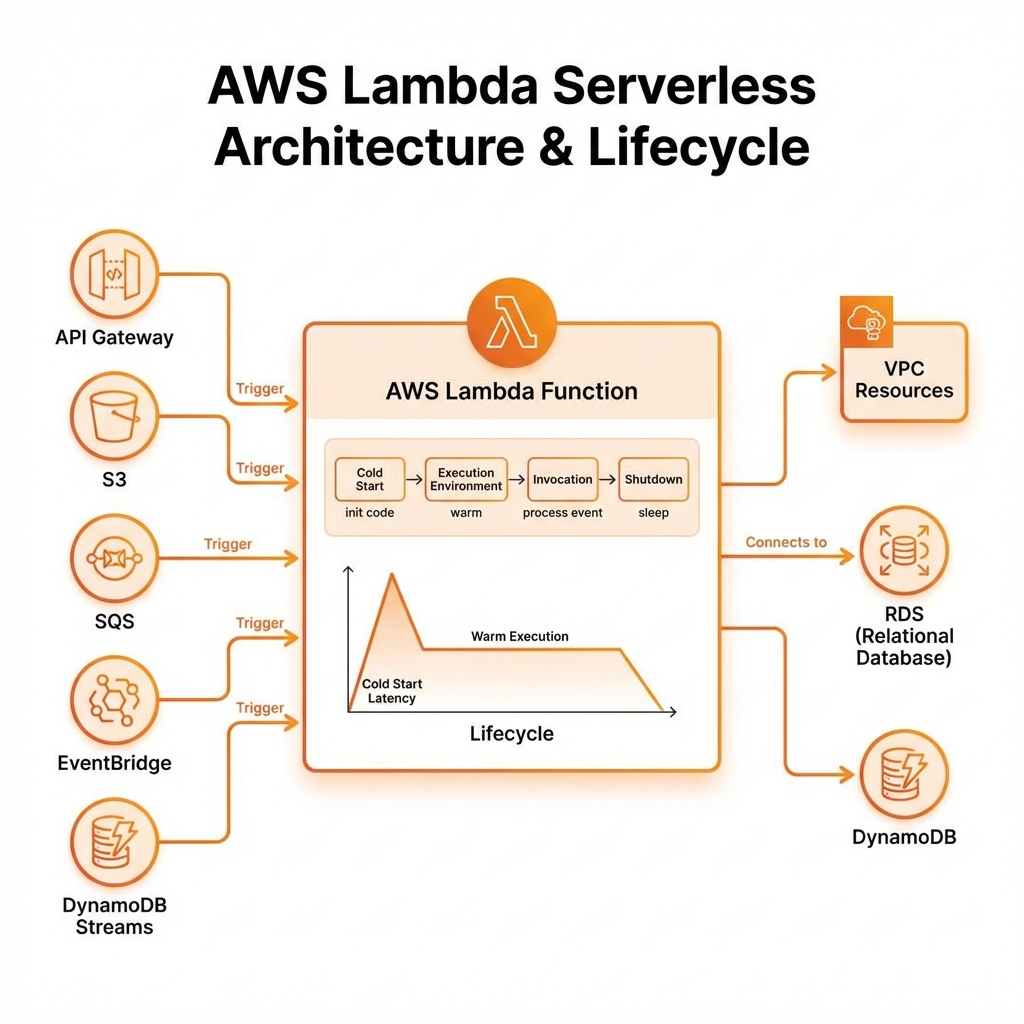
Lambda with AWS CDK
// AWS CDK: Lambda with API Gateway and DynamoDB
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import * as lambda from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-lambda';
import * as apigw from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-apigateway';
import * as dynamodb from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-dynamodb';
export class LambdaStack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
// DynamoDB table
const table = new dynamodb.Table(this, 'ItemsTable', {
partitionKey: { name: 'id', type: dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING },
billingMode: dynamodb.BillingMode.PAY_PER_REQUEST,
removalPolicy: cdk.RemovalPolicy.DESTROY,
});
// Lambda function
const handler = new lambda.Function(this, 'ApiHandler', {
runtime: lambda.Runtime.NODEJS_18_X,
code: lambda.Code.fromAsset('lambda'),
handler: 'index.handler',
memorySize: 256,
timeout: cdk.Duration.seconds(30),
environment: {
TABLE_NAME: table.tableName,
},
tracing: lambda.Tracing.ACTIVE, // X-Ray tracing
});
// Grant permissions
table.grantReadWriteData(handler);
// Provisioned Concurrency for low latency
const version = handler.currentVersion;
const alias = new lambda.Alias(this, 'ProdAlias', {
aliasName: 'prod',
version,
provisionedConcurrentExecutions: 5,
});
// API Gateway
const api = new apigw.RestApi(this, 'ItemsApi', {
restApiName: 'Items Service',
deployOptions: {
stageName: 'prod',
throttlingRateLimit: 1000,
throttlingBurstLimit: 2000,
},
});
const items = api.root.addResource('items');
items.addMethod('GET', new apigw.LambdaIntegration(alias));
items.addMethod('POST', new apigw.LambdaIntegration(alias));
const item = items.addResource('{id}');
item.addMethod('GET', new apigw.LambdaIntegration(alias));
}
}Lambda Function Code (Python)
# lambda/handler.py - Lambda function with best practices
import json
import os
import boto3
from aws_lambda_powertools import Logger, Tracer, Metrics
from aws_lambda_powertools.event_handler import APIGatewayRestResolver
from aws_lambda_powertools.utilities.typing import LambdaContext
logger = Logger()
tracer = Tracer()
metrics = Metrics()
app = APIGatewayRestResolver()
# Initialize outside handler for connection reuse
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
table = dynamodb.Table(os.environ['TABLE_NAME'])
@app.get("/items")
@tracer.capture_method
def get_items():
response = table.scan(Limit=100)
return {"items": response.get('Items', [])}
@app.get("/items/")
@tracer.capture_method
def get_item(item_id: str):
response = table.get_item(Key={'id': item_id})
if 'Item' not in response:
return {"error": "Item not found"}, 404
return response['Item']
@app.post("/items")
@tracer.capture_method
def create_item():
body = app.current_event.json_body
table.put_item(Item=body)
metrics.add_metric(name="ItemsCreated", unit="Count", value=1)
return {"message": "Created", "id": body.get('id')}, 201
@logger.inject_lambda_context
@tracer.capture_lambda_handler
@metrics.log_metrics(capture_cold_start_metric=True)
def handler(event: dict, context: LambdaContext) -> dict:
return app.resolve(event, context) - Initialize SDK clients outside the handler for connection reuse
- Use Provisioned Concurrency for consistent latency
- Set appropriate memory (CPU scales with memory)
- Use Lambda Powertools for observability
- Keep deployment packages small (<50MB unzipped)
| Execution timeout | 15 minutes maximum |
| Memory | 128 MB – 10,240 MB (10 GB) |
| Ephemeral storage (/tmp) | 512 MB – 10,240 MB |
| Deployment package | 50 MB zipped, 250 MB unzipped |
| Container image | 10 GB maximum |
| Concurrent executions | 1,000 per region (soft limit) |
| Burst concurrency | 500-3,000 depending on region |
| Environment variables | 4 KB total size |
| Layers | 5 layers, 250 MB total unzipped |
| Payload size (sync) | 6 MB request/response |
| Payload size (async) | 256 KB |
Note: CPU power scales linearly with memory. At 1,769 MB, you get 1 full vCPU. For CPU-intensive tasks, increase memory even if you don't need the RAM.
Container Services: ECS & EKS
AWS offers two container orchestration services: ECS (AWS-native) and EKS (managed Kubernetes). Both can run on EC2 instances or Fargate (serverless containers).
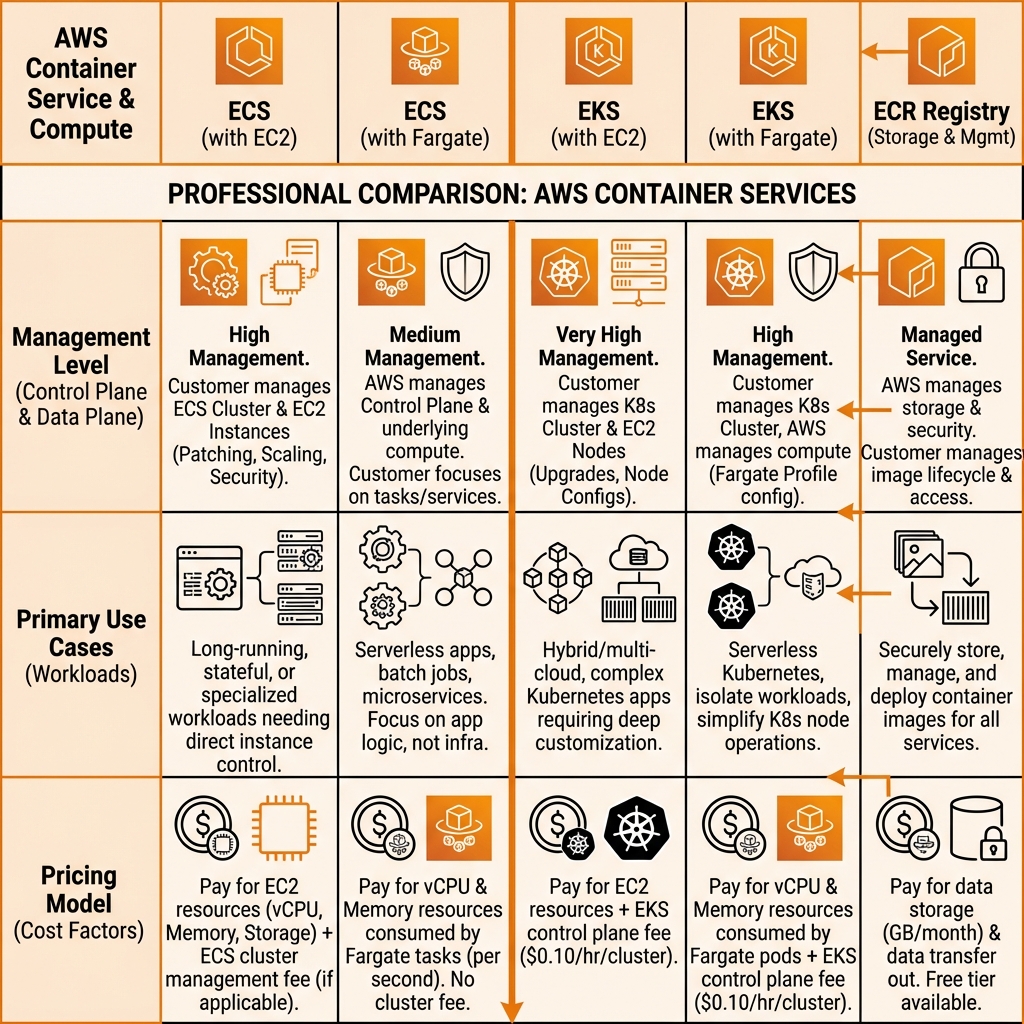
ECS Fargate with AWS CDK
// AWS CDK: ECS Fargate Service with ALB
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import * as ecs from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-ecs';
import * as ecs_patterns from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-ecs-patterns';
import * as ecr from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-ecr';
export class EcsStack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
// ECS Cluster
const cluster = new ecs.Cluster(this, 'AppCluster', {
clusterName: 'app-cluster',
containerInsights: true,
});
// Fargate Service with ALB (L3 construct)
const service = new ecs_patterns.ApplicationLoadBalancedFargateService(
this, 'AppService', {
cluster,
cpu: 512,
memoryLimitMiB: 1024,
desiredCount: 2,
taskImageOptions: {
image: ecs.ContainerImage.fromRegistry('nginx:latest'),
containerPort: 80,
environment: {
NODE_ENV: 'production',
},
},
publicLoadBalancer: true,
circuitBreaker: { rollback: true },
}
);
// Auto Scaling
const scaling = service.service.autoScaleTaskCount({
minCapacity: 2,
maxCapacity: 10,
});
scaling.scaleOnCpuUtilization('CpuScaling', {
targetUtilizationPercent: 70,
scaleInCooldown: cdk.Duration.minutes(5),
scaleOutCooldown: cdk.Duration.minutes(2),
});
scaling.scaleOnRequestCount('RequestScaling', {
requestsPerTarget: 1000,
targetGroup: service.targetGroup,
});
}
}EKS with Terraform
# Terraform: EKS Cluster with managed node groups
module "eks" {
source = "terraform-aws-modules/eks/aws"
version = "~> 19.0"
cluster_name = "app-cluster"
cluster_version = "1.28"
vpc_id = module.vpc.vpc_id
subnet_ids = module.vpc.private_subnets
cluster_endpoint_public_access = true
# Enable IRSA (IAM Roles for Service Accounts)
enable_irsa = true
eks_managed_node_groups = {
general = {
desired_size = 2
min_size = 2
max_size = 10
instance_types = ["m6i.large", "m5.large"]
capacity_type = "ON_DEMAND"
labels = {
role = "general"
}
}
spot = {
desired_size = 2
min_size = 0
max_size = 20
instance_types = ["m6i.large", "m5.large", "m5a.large"]
capacity_type = "SPOT"
labels = {
role = "spot-workers"
}
taints = [{
key = "spot"
value = "true"
effect = "NO_SCHEDULE"
}]
}
}
# Cluster addons
cluster_addons = {
coredns = {
most_recent = true
}
kube-proxy = {
most_recent = true
}
vpc-cni = {
most_recent = true
}
}
}
# Karpenter for advanced autoscaling (optional)
module "karpenter" {
source = "terraform-aws-modules/eks/aws//modules/karpenter"
version = "~> 19.0"
cluster_name = module.eks.cluster_name
irsa_oidc_provider_arn = module.eks.oidc_provider_arn
}Key Takeaways
- ✅ Right-size EC2 - Use Compute Optimizer recommendations; Graviton (ARM) saves 20-40%
- ✅ Lambda for event-driven - Ideal for APIs, data processing, scheduled tasks <15 min
- ✅ ECS for simplicity - AWS-native, easier than K8s for most use cases
- ✅ EKS for Kubernetes - When you need K8s ecosystem or multi-cloud portability
- ✅ Fargate for serverless containers - No node management, pay per task
- ✅ Use Spot instances - Up to 90% savings for fault-tolerant workloads
Conclusion
AWS compute services provide options for every workload type. EC2 offers maximum control, Lambda eliminates all infrastructure management, and container services (ECS/EKS) provide the middle ground. In Part 3, we'll explore AWS storage and database services including S3, RDS, DynamoDB, and more.
References
- EC2 Instance Types
- Lambda Best Practices
- ECS Best Practices Guide
- EKS Best Practices
- Lambda Powertools
Discover more from C4: Container, Code, Cloud & Context
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.