Networking is the foundation of every AWS architecture. This guide covers VPC design, DNS with Route 53, content delivery with CloudFront, and load balancing—with production-ready code examples.
AWS Networking Services Overview
AWS networking services enable you to build secure, scalable, and globally distributed applications. From VPCs for network isolation to CloudFront for global content delivery.
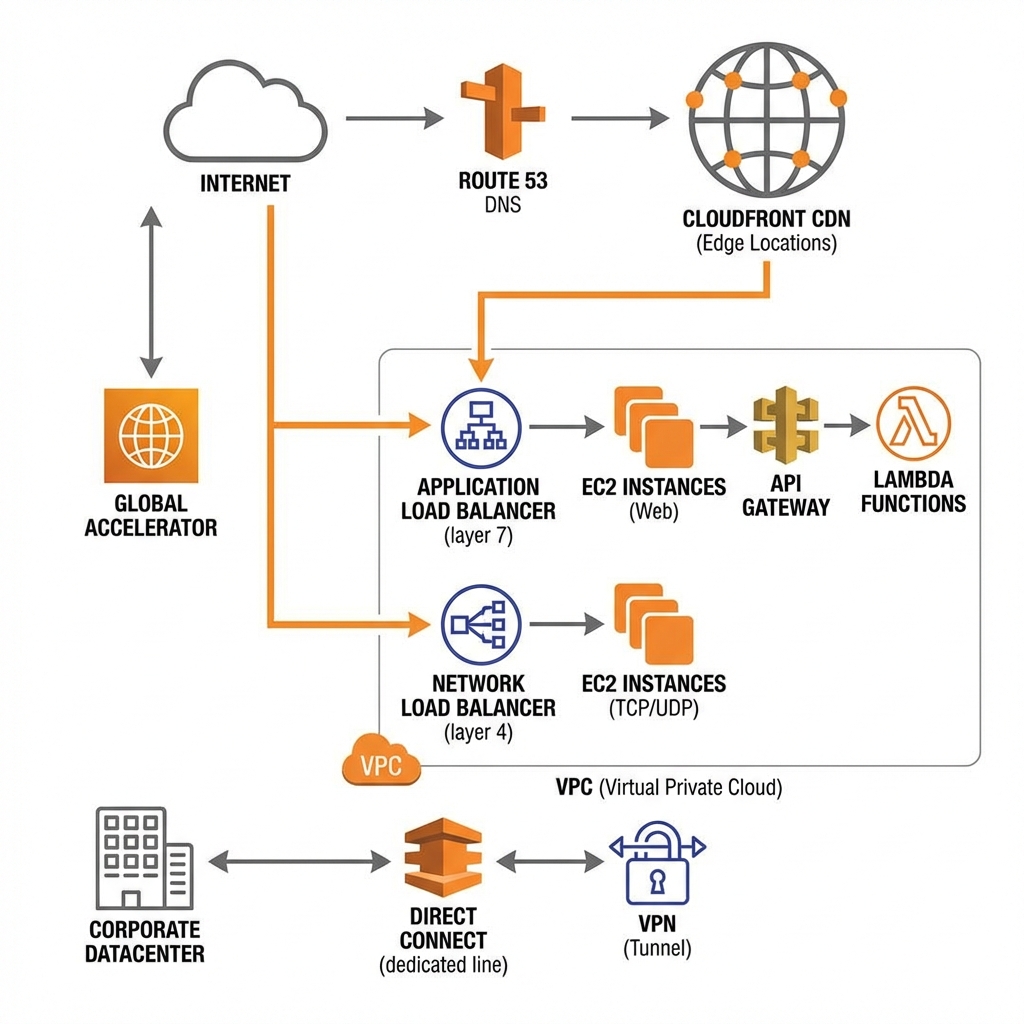
Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)
VPC is your isolated network in AWS. You control IP addressing, subnets, route tables, and network gateways. Every resource you launch runs inside a VPC.
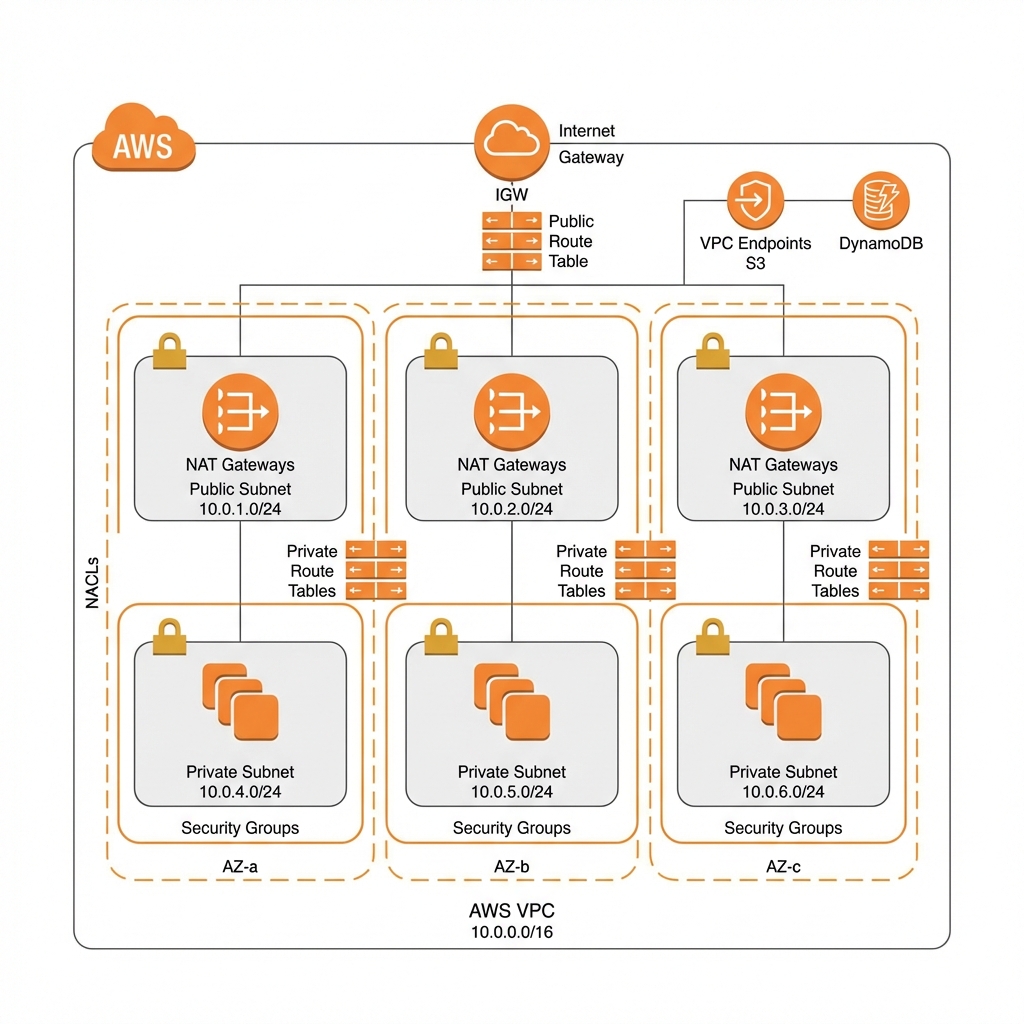
VPC Design Best Practices
| Component | Best Practice | Why |
|---|---|---|
| CIDR Block | Use /16 for VPC, /24 for subnets | Room to grow, avoid overlap with on-prem |
| Subnets | Minimum 2 AZs, prefer 3 | High availability, AZ failure tolerance |
| NAT Gateway | One per AZ for HA | Avoid single point of failure |
| VPC Endpoints | Use for S3, DynamoDB, ECR | Private traffic, reduce NAT costs |
| Flow Logs | Enable on all VPCs | Security analysis, troubleshooting |
VPC with AWS CDK
// AWS CDK: Production VPC with all best practices
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import * as ec2 from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-ec2';
import * as logs from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-logs';
export class VpcStack extends cdk.Stack {
public readonly vpc: ec2.Vpc;
constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
// Production VPC
this.vpc = new ec2.Vpc(this, 'ProductionVpc', {
ipAddresses: ec2.IpAddresses.cidr('10.0.0.0/16'),
maxAzs: 3,
// NAT Gateway per AZ for high availability
natGateways: 3,
subnetConfiguration: [
{
cidrMask: 24,
name: 'Public',
subnetType: ec2.SubnetType.PUBLIC,
},
{
cidrMask: 24,
name: 'Private',
subnetType: ec2.SubnetType.PRIVATE_WITH_EGRESS,
},
{
cidrMask: 24,
name: 'Isolated',
subnetType: ec2.SubnetType.PRIVATE_ISOLATED,
},
],
// VPC Flow Logs
flowLogs: {
'FlowLog': {
destination: ec2.FlowLogDestination.toCloudWatchLogs(
new logs.LogGroup(this, 'VpcFlowLogs', {
retention: logs.RetentionDays.ONE_MONTH,
})
),
trafficType: ec2.FlowLogTrafficType.ALL,
},
},
});
// Gateway endpoints (free, no NAT charges)
this.vpc.addGatewayEndpoint('S3Endpoint', {
service: ec2.GatewayVpcEndpointAwsService.S3,
});
this.vpc.addGatewayEndpoint('DynamoDbEndpoint', {
service: ec2.GatewayVpcEndpointAwsService.DYNAMODB,
});
// Interface endpoints (for services like ECR, Secrets Manager)
this.vpc.addInterfaceEndpoint('EcrDockerEndpoint', {
service: ec2.InterfaceVpcEndpointAwsService.ECR_DOCKER,
});
this.vpc.addInterfaceEndpoint('SecretsManagerEndpoint', {
service: ec2.InterfaceVpcEndpointAwsService.SECRETS_MANAGER,
});
}
}VPC with Terraform
# Terraform: Production VPC using AWS VPC module
module "vpc" {
source = "terraform-aws-modules/vpc/aws"
version = "~> 5.0"
name = "production-vpc"
cidr = "10.0.0.0/16"
azs = ["us-east-1a", "us-east-1b", "us-east-1c"]
private_subnets = ["10.0.1.0/24", "10.0.2.0/24", "10.0.3.0/24"]
public_subnets = ["10.0.101.0/24", "10.0.102.0/24", "10.0.103.0/24"]
database_subnets = ["10.0.201.0/24", "10.0.202.0/24", "10.0.203.0/24"]
# NAT Gateway - one per AZ
enable_nat_gateway = true
single_nat_gateway = false
one_nat_gateway_per_az = true
# DNS settings
enable_dns_hostnames = true
enable_dns_support = true
# VPC Flow Logs
enable_flow_log = true
create_flow_log_cloudwatch_log_group = true
create_flow_log_cloudwatch_iam_role = true
flow_log_max_aggregation_interval = 60
# Tags for EKS if needed
public_subnet_tags = {
"kubernetes.io/role/elb" = 1
}
private_subnet_tags = {
"kubernetes.io/role/internal-elb" = 1
}
}
# VPC Endpoints
module "vpc_endpoints" {
source = "terraform-aws-modules/vpc/aws//modules/vpc-endpoints"
version = "~> 5.0"
vpc_id = module.vpc.vpc_id
endpoints = {
s3 = {
service = "s3"
service_type = "Gateway"
route_table_ids = module.vpc.private_route_table_ids
}
dynamodb = {
service = "dynamodb"
service_type = "Gateway"
route_table_ids = module.vpc.private_route_table_ids
}
}
}- 5 VPCs per region (soft limit, can increase)
- 200 subnets per VPC
- NAT Gateway: ~$32/month + $0.045/GB processed
- Interface Endpoint: ~$7.30/month + $0.01/GB
- VPC Peering: Free within region, $0.01/GB cross-region
Amazon Route 53
Route 53 is AWS’s highly available DNS service. It offers domain registration, DNS routing, and health checking with 100% availability SLA.
Route 53 Routing Policies
| Policy | Use Case | How It Works |
|---|---|---|
| Simple | Single resource | Returns one or all values randomly |
| Weighted | Blue/green, A/B testing | Route % of traffic to each endpoint |
| Latency | Multi-region apps | Route to lowest latency region |
| Failover | Active-passive DR | Route to secondary if primary fails |
| Geolocation | Content localization | Route based on user location |
| Multivalue | Simple load balancing | Return multiple healthy IPs |
# Terraform: Route 53 with health checks and failover
resource "aws_route53_zone" "main" {
name = "example.com"
}
# Health check for primary
resource "aws_route53_health_check" "primary" {
fqdn = "primary.example.com"
port = 443
type = "HTTPS"
resource_path = "/health"
failure_threshold = 3
request_interval = 30
tags = {
Name = "primary-health-check"
}
}
# Primary record with failover
resource "aws_route53_record" "primary" {
zone_id = aws_route53_zone.main.zone_id
name = "app.example.com"
type = "A"
alias {
name = aws_lb.primary.dns_name
zone_id = aws_lb.primary.zone_id
evaluate_target_health = true
}
failover_routing_policy {
type = "PRIMARY"
}
set_identifier = "primary"
health_check_id = aws_route53_health_check.primary.id
}
# Secondary (failover) record
resource "aws_route53_record" "secondary" {
zone_id = aws_route53_zone.main.zone_id
name = "app.example.com"
type = "A"
alias {
name = aws_lb.secondary.dns_name
zone_id = aws_lb.secondary.zone_id
evaluate_target_health = true
}
failover_routing_policy {
type = "SECONDARY"
}
set_identifier = "secondary"
}Amazon CloudFront
CloudFront is AWS’s global CDN with 600+ edge locations. It accelerates static and dynamic content, provides DDoS protection, and reduces origin load.
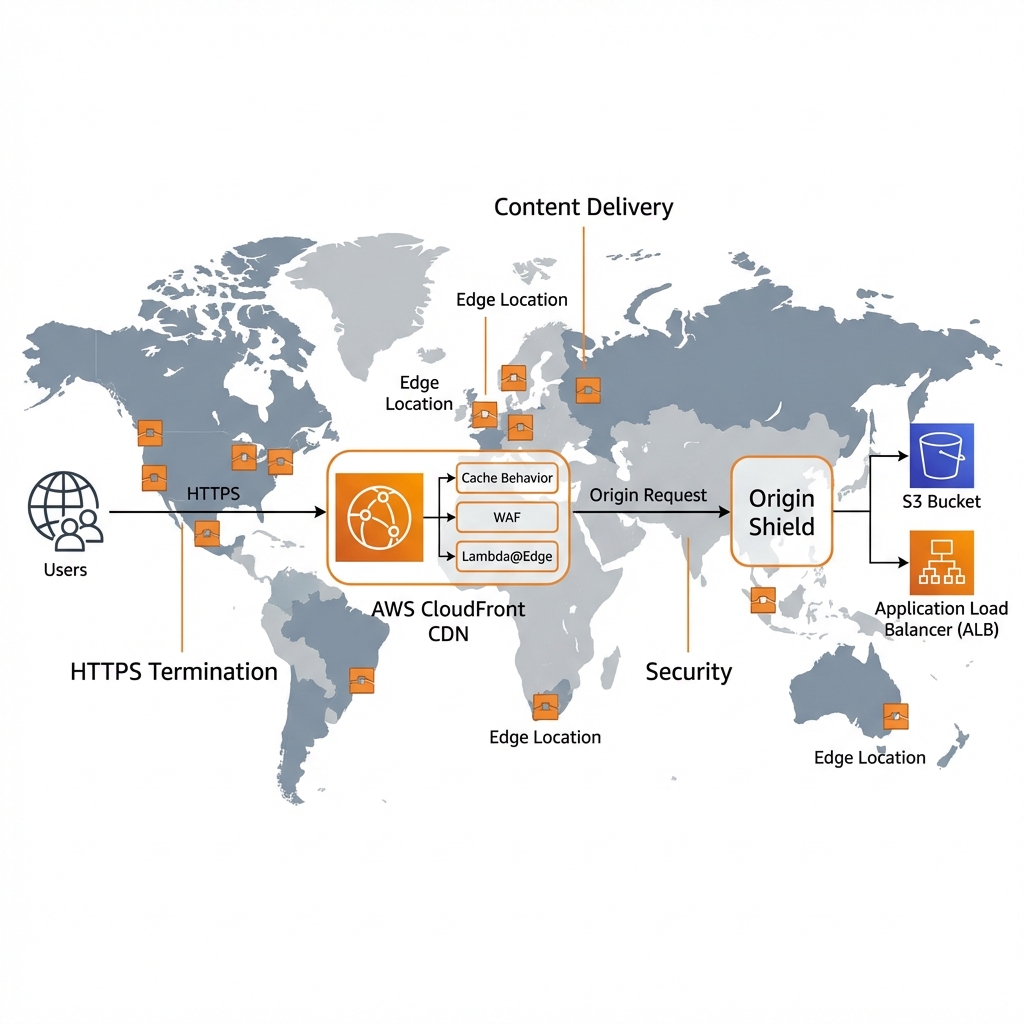
CloudFront with AWS CDK
// AWS CDK: CloudFront distribution with S3 origin
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import * as cloudfront from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-cloudfront';
import * as origins from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-cloudfront-origins';
import * as s3 from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-s3';
import * as acm from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-certificatemanager';
export class CloudFrontStack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
// S3 bucket for static content
const bucket = new s3.Bucket(this, 'WebsiteBucket', {
blockPublicAccess: s3.BlockPublicAccess.BLOCK_ALL,
encryption: s3.BucketEncryption.S3_MANAGED,
});
// CloudFront OAC (Origin Access Control)
const oac = new cloudfront.S3OriginAccessControl(this, 'OAC', {
signing: cloudfront.Signing.SIGV4_ALWAYS,
});
// Distribution
const distribution = new cloudfront.Distribution(this, 'Distribution', {
defaultBehavior: {
origin: origins.S3BucketOrigin.withOriginAccessControl(bucket, {
originAccessControl: oac,
}),
viewerProtocolPolicy: cloudfront.ViewerProtocolPolicy.REDIRECT_TO_HTTPS,
cachePolicy: cloudfront.CachePolicy.CACHING_OPTIMIZED,
compress: true,
},
// Custom domain (optional)
// domainNames: ['cdn.example.com'],
// certificate: acm.Certificate.fromCertificateArn(this, 'Cert', certArn),
defaultRootObject: 'index.html',
// Price class (use all edge locations or subset)
priceClass: cloudfront.PriceClass.PRICE_CLASS_100,
// Error responses
errorResponses: [
{
httpStatus: 404,
responseHttpStatus: 200,
responsePagePath: '/index.html', // SPA routing
ttl: cdk.Duration.minutes(5),
},
],
// Origin Shield for cache efficiency
enableLogging: true,
});
// API behavior (for dynamic content)
distribution.addBehavior('/api/*', new origins.HttpOrigin('api.example.com'), {
viewerProtocolPolicy: cloudfront.ViewerProtocolPolicy.HTTPS_ONLY,
cachePolicy: cloudfront.CachePolicy.CACHING_DISABLED,
originRequestPolicy: cloudfront.OriginRequestPolicy.ALL_VIEWER,
allowedMethods: cloudfront.AllowedMethods.ALLOW_ALL,
});
}
}Load Balancing: ALB vs NLB
| Feature | ALB (Application) | NLB (Network) |
|---|---|---|
| Layer | Layer 7 (HTTP/HTTPS) | Layer 4 (TCP/UDP) |
| Latency | ~400ms added | ~100μs added |
| Static IP | No (use Global Accelerator) | Yes (Elastic IP support) |
| Path routing | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Host routing | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| WebSocket | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Best For | Web apps, microservices | IoT, gaming, real-time |
Key Takeaways
- ✅ Design VPCs for HA – Use 3 AZs, NAT Gateway per AZ, VPC endpoints
- ✅ Use private subnets – Only ALBs and NAT Gateways in public subnets
- ✅ Enable Flow Logs – Essential for security and troubleshooting
- ✅ CloudFront for everything – Even dynamic APIs benefit from edge caching
- ✅ ALB for HTTP, NLB for TCP – Choose based on protocol requirements
- ✅ Use Route 53 health checks – Automatic failover for DR
Conclusion
AWS networking provides the foundation for secure, scalable applications. VPCs isolate your resources, Route 53 provides reliable DNS, CloudFront accelerates content globally, and load balancers distribute traffic. In Part 5, we’ll explore AWS security services including KMS, WAF, and Shield.
References
Discover more from C4: Container, Code, Cloud & Context
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.