Infrastructure as Code (IaC) enables you to manage AWS resources through code, providing version control, repeatability, and collaboration. This guide compares AWS CDK, CloudFormation, and Terraform with production-ready examples.
AWS DevOps & IaC Overview
AWS provides multiple options for Infrastructure as Code and CI/CD. Your choice depends on team skills, multi-cloud requirements, and preference for declarative vs imperative approaches.
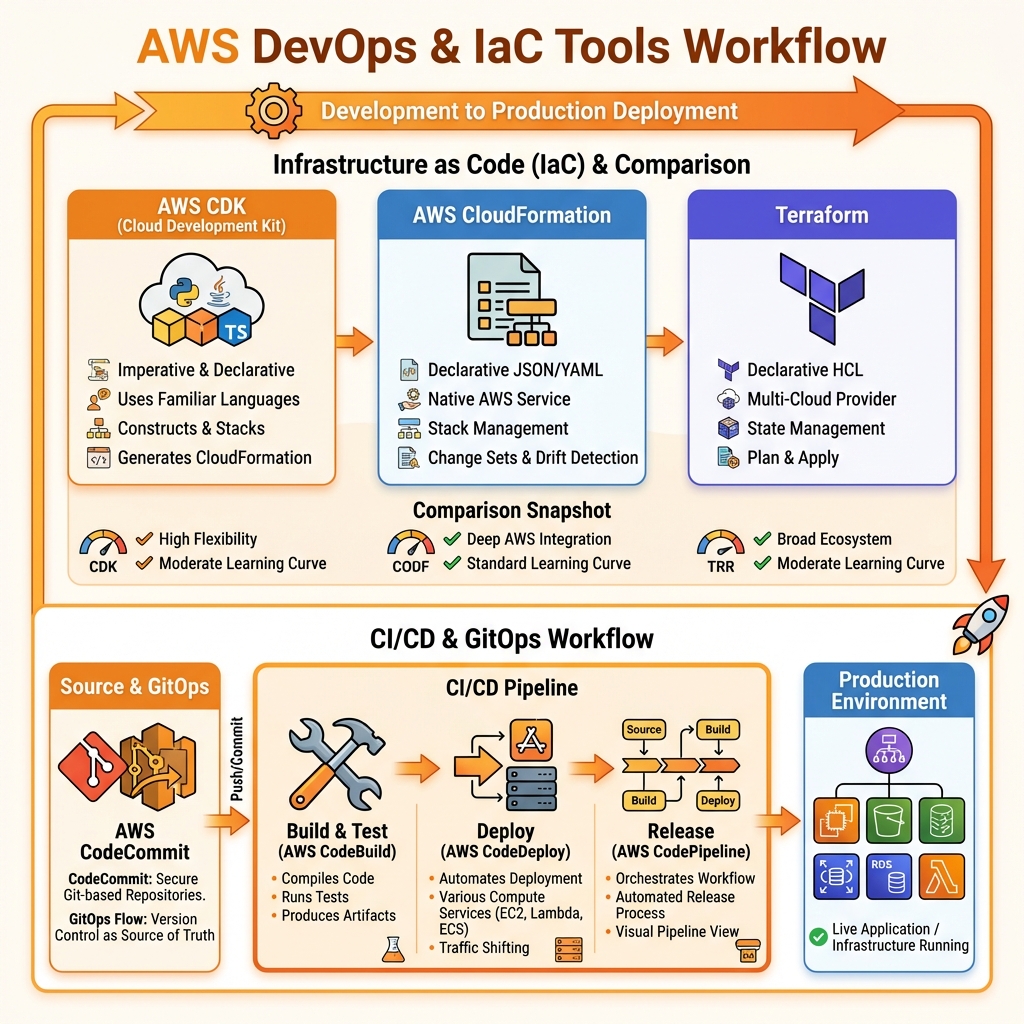
IaC Tool Comparison
| Feature | AWS CDK | CloudFormation | Terraform |
|---|---|---|---|
| Language | TypeScript, Python, Java, C#, Go | JSON/YAML | HCL |
| Approach | Imperative → Declarative | Declarative | Declarative |
| Cloud Support | AWS only | AWS only | Multi-cloud |
| State Management | CloudFormation (AWS-managed) | AWS-managed | Local/Remote (S3, TFC) |
| Drift Detection | ✅ Native | ✅ Native | ✅ terraform plan |
| Best For | Developers, complex logic | AWS-native, simple stacks | Multi-cloud, platform teams |
AWS CDK Deep Dive
AWS CDK lets you define infrastructure using familiar programming languages. It synthesizes to CloudFormation, giving you the best of both worlds: programming flexibility and AWS-native deployment.
CDK Project Structure
# Initialize a new CDK project
mkdir my-cdk-app && cd my-cdk-app
npx cdk init app --language typescript
# Project structure
my-cdk-app/
├── bin/
│ └── my-cdk-app.ts # App entry point
├── lib/
│ └── my-cdk-app-stack.ts # Stack definition
├── test/
│ └── my-cdk-app.test.ts # Tests
├── cdk.json # CDK config
├── package.json
└── tsconfig.json
# Common CDK commands
cdk synth # Generate CloudFormation template
cdk diff # Preview changes
cdk deploy # Deploy stack
cdk destroy # Delete stack
cdk bootstrap # Initialize CDK in account/regionComplete CDK Application Example
// lib/full-stack.ts - Complete serverless application
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import * as apigateway from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-apigateway';
import * as lambda from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-lambda';
import * as dynamodb from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-dynamodb';
import * as s3 from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-s3';
import * as cloudfront from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-cloudfront';
import * as origins from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-cloudfront-origins';
import { Construct } from 'constructs';
export interface FullStackProps extends cdk.StackProps {
environment: 'dev' | 'staging' | 'prod';
}
export class FullStackApplication extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props: FullStackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
const isProd = props.environment === 'prod';
// DynamoDB table
const table = new dynamodb.Table(this, 'DataTable', {
partitionKey: { name: 'pk', type: dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING },
sortKey: { name: 'sk', type: dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING },
billingMode: isProd
? dynamodb.BillingMode.PROVISIONED
: dynamodb.BillingMode.PAY_PER_REQUEST,
pointInTimeRecovery: isProd,
removalPolicy: isProd
? cdk.RemovalPolicy.RETAIN
: cdk.RemovalPolicy.DESTROY,
});
if (isProd) {
table.autoScaleReadCapacity({
minCapacity: 5,
maxCapacity: 100,
}).scaleOnUtilization({ targetUtilizationPercent: 70 });
}
// Lambda function
const handler = new lambda.Function(this, 'ApiHandler', {
runtime: lambda.Runtime.NODEJS_18_X,
code: lambda.Code.fromAsset('lambda'),
handler: 'api.handler',
memorySize: isProd ? 512 : 256,
timeout: cdk.Duration.seconds(30),
environment: {
TABLE_NAME: table.tableName,
ENVIRONMENT: props.environment,
},
tracing: isProd ? lambda.Tracing.ACTIVE : lambda.Tracing.DISABLED,
});
table.grantReadWriteData(handler);
// API Gateway
const api = new apigateway.RestApi(this, 'Api', {
restApiName: `api-${props.environment}`,
deployOptions: {
stageName: props.environment,
throttlingRateLimit: isProd ? 10000 : 1000,
throttlingBurstLimit: isProd ? 5000 : 500,
},
});
api.root.addResource('items').addMethod('GET',
new apigateway.LambdaIntegration(handler)
);
// Static website bucket
const websiteBucket = new s3.Bucket(this, 'WebsiteBucket', {
blockPublicAccess: s3.BlockPublicAccess.BLOCK_ALL,
encryption: s3.BucketEncryption.S3_MANAGED,
removalPolicy: cdk.RemovalPolicy.DESTROY,
autoDeleteObjects: !isProd,
});
// CloudFront distribution
const distribution = new cloudfront.Distribution(this, 'Distribution', {
defaultBehavior: {
origin: origins.S3BucketOrigin.withOriginAccessControl(websiteBucket),
viewerProtocolPolicy: cloudfront.ViewerProtocolPolicy.REDIRECT_TO_HTTPS,
},
additionalBehaviors: {
'/api/*': {
origin: new origins.HttpOrigin(`${api.restApiId}.execute-api.${this.region}.amazonaws.com`),
viewerProtocolPolicy: cloudfront.ViewerProtocolPolicy.HTTPS_ONLY,
cachePolicy: cloudfront.CachePolicy.CACHING_DISABLED,
originRequestPolicy: cloudfront.OriginRequestPolicy.ALL_VIEWER_EXCEPT_HOST_HEADER,
},
},
});
// Outputs
new cdk.CfnOutput(this, 'ApiUrl', { value: api.url });
new cdk.CfnOutput(this, 'DistributionUrl', {
value: `https://${distribution.distributionDomainName}`
});
}
}AWS CI/CD Pipeline
AWS CodePipeline orchestrates your CI/CD workflow, integrating source control, build, test, and deployment stages.
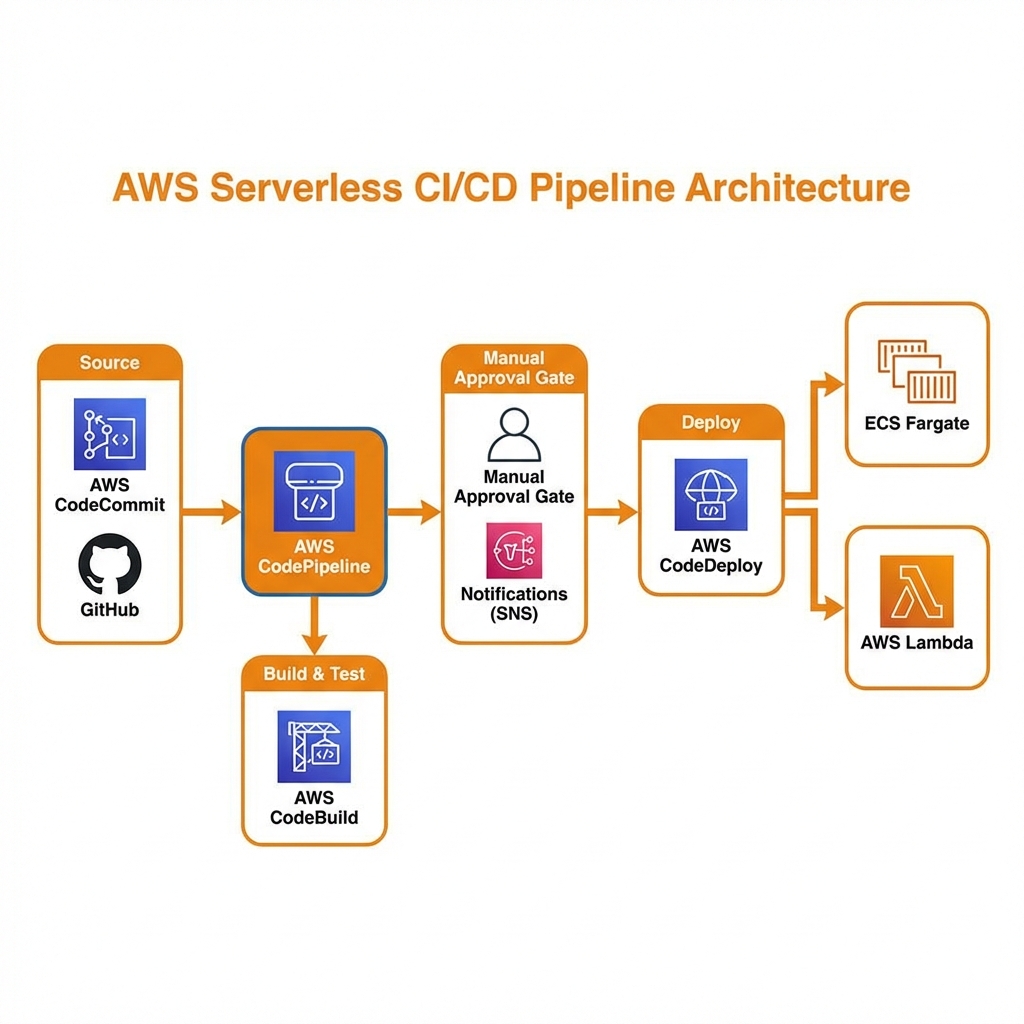
CDK Pipeline with Self-Mutating Updates
// lib/pipeline-stack.ts - Self-mutating CDK Pipeline
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import * as pipelines from 'aws-cdk-lib/pipelines';
import { Construct } from 'constructs';
export class PipelineStack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
const pipeline = new pipelines.CodePipeline(this, 'Pipeline', {
pipelineName: 'MyAppPipeline',
synth: new pipelines.ShellStep('Synth', {
input: pipelines.CodePipelineSource.gitHub('owner/repo', 'main', {
authentication: cdk.SecretValue.secretsManager('github-token'),
}),
commands: [
'npm ci',
'npm run build',
'npm run test',
'npx cdk synth',
],
}),
dockerEnabledForSynth: true,
crossAccountKeys: true,
});
// Development stage
const devStage = pipeline.addStage(new MyApplicationStage(this, 'Dev', {
env: { account: '111111111111', region: 'us-east-1' },
}));
devStage.addPost(
new pipelines.ShellStep('IntegrationTests', {
commands: ['npm run test:integration'],
})
);
// Production stage with manual approval
const prodStage = pipeline.addStage(new MyApplicationStage(this, 'Prod', {
env: { account: '222222222222', region: 'us-east-1' },
}));
prodStage.addPre(
new pipelines.ManualApprovalStep('PromoteToProd', {
comment: 'Ready to deploy to production?',
})
);
}
}Terraform on AWS
Terraform is ideal for multi-cloud environments or teams with existing Terraform experience. Use remote state in S3 with DynamoDB locking for team collaboration.
Terraform Best Practices Structure
# Backend configuration for team collaboration
# backend.tf
terraform {
required_version = ">= 1.5"
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 5.0"
}
}
backend "s3" {
bucket = "my-terraform-state-bucket"
key = "prod/terraform.tfstate"
region = "us-east-1"
dynamodb_table = "terraform-locks"
encrypt = true
}
}
# variables.tf
variable "environment" {
type = string
description = "Environment name"
validation {
condition = contains(["dev", "staging", "prod"], var.environment)
error_message = "Environment must be dev, staging, or prod."
}
}
variable "vpc_cidr" {
type = string
default = "10.0.0.0/16"
description = "VPC CIDR block"
}
# locals.tf
locals {
common_tags = {
Environment = var.environment
Project = "my-app"
ManagedBy = "terraform"
}
is_prod = var.environment == "prod"
}
# main.tf
module "vpc" {
source = "terraform-aws-modules/vpc/aws"
version = "~> 5.0"
name = "${var.environment}-vpc"
cidr = var.vpc_cidr
azs = ["us-east-1a", "us-east-1b", "us-east-1c"]
private_subnets = ["10.0.1.0/24", "10.0.2.0/24", "10.0.3.0/24"]
public_subnets = ["10.0.101.0/24", "10.0.102.0/24", "10.0.103.0/24"]
enable_nat_gateway = true
single_nat_gateway = !local.is_prod
one_nat_gateway_per_az = local.is_prod
tags = local.common_tags
}
# outputs.tf
output "vpc_id" {
value = module.vpc.vpc_id
description = "VPC ID"
}
output "private_subnet_ids" {
value = module.vpc.private_subnets
description = "Private subnet IDs"
}- Use remote state (S3 + DynamoDB for Terraform)
- Implement state locking to prevent concurrent changes
- Use workspaces or separate state files per environment
- Pin provider/module versions for reproducibility
- Run
planin CI,applyonly after approval - Use OIDC for CI/CD authentication (no long-lived keys)
GitHub Actions for AWS
# .github/workflows/deploy.yml
name: Deploy to AWS
on:
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches: [main]
permissions:
id-token: write # For OIDC
contents: read
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Configure AWS credentials (OIDC)
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v4
with:
role-to-assume: arn:aws:iam::${{ secrets.AWS_ACCOUNT_ID }}:role/GitHubActionsRole
aws-region: us-east-1
- name: Setup Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: '18'
cache: 'npm'
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm ci
- name: Run tests
run: npm test
- name: CDK Diff
if: github.event_name == 'pull_request'
run: npx cdk diff
- name: CDK Deploy
if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/main'
run: npx cdk deploy --all --require-approval neverKey Takeaways
- ✅ CDK for developers – Programming languages, IDE support, type safety
- ✅ CloudFormation for AWS-native – No additional tooling, deep integration
- ✅ Terraform for multi-cloud – Consistent workflow across providers
- ✅ Use OIDC for CI/CD – No long-lived credentials in pipelines
- ✅ Remote state is mandatory – Enables team collaboration
- ✅ Test infrastructure code – CDK has built-in testing support
Conclusion
Congratulations on completing the AWS Fundamentals Series! You now have comprehensive knowledge of AWS core services: account structure, compute, storage, databases, networking, security, and infrastructure as code. Apply these concepts iteratively—start with simple architectures and evolve as your needs grow. Remember: the best architecture is one that solves your specific problems while remaining maintainable and cost-effective.
Series Recap
- Part 1: AWS Organizations, IAM, global infrastructure
- Part 2: EC2, Lambda, ECS, EKS compute options
- Part 3: S3, RDS, DynamoDB, Aurora storage & databases
- Part 4: VPC, Route 53, CloudFront, load balancers
- Part 5: KMS, WAF, Shield, GuardDuty security
- Part 6: CDK, CloudFormation, Terraform, CI/CD (this article)
References
- AWS CDK Developer Guide
- AWS CloudFormation User Guide
- Terraform Documentation
- AWS CodePipeline User Guide
- CDK Pipelines Documentation
Discover more from C4: Container, Code, Cloud & Context
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.